CROHN’S DISEASE, Nathan Fox, MD (Digital)
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)

Crohn’s Disease
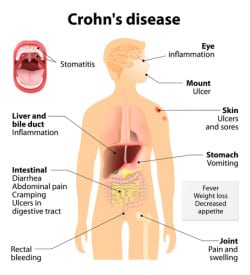
Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease, which can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the rectum. However, most CD cases affect the small bowel, colon, or both.The symptoms of CD depend on the area it involves, and may include pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, fistulas, abscesses, and poor weight gain. General treatments of CD include medical immunomodulation combined with surgical resection.
Most women with CD during pregnancy do well, especially if they did not have active disease around the time of conception. However, for women with active disease, issues during pregnancy may include poor nutrition and weight gain, impaired fetal growth, medication exposures, and mode of delivery.
Nutrition and Weight Gain
If CD is controlled, women generally have normal weight gain. However, a nutritional consultation is often helpful, specifically for patients with poor weight gain or with severe CD.
Fetal Growth
Women with CD have a higher chance of delivering small infants. The restriction in fetal growth may be due to nutritional factors, medication use, or disease activity. Based on this, we generally recommend serial growth ultrasounds in the third trimester.
Medication Use
Fortunately, most medications prescribed for CD are considered safe during pregnancy. However, some medication use may potentially be associated with some risk. These should be discussed with your doctors prior to pregnancy, if possible.
Delivery
Cesarean delivery is often suggested for patients with perianal disease to avoid lacerations in the perianal and perineum area. For patients without perianal disease, vaginal delivery is usually an option. Some patients with extensive abdominal adhesions may need a cesarean delivery along with support from a general surgeon with expertise in CD.
Maternal Fetal Medicine blogs are intended for educational purposes only and do not replace certified professional care. Medical conditions vary and change frequently. Please ask your doctor any questions you may have regarding your condition to receive a proper diagnosis or risk analysis. Thank you!